HTTP vs HTTPS: What’s The Difference Between Them?

When browsing the internet, have you ever stopped to think about the security of the website you are visiting? The protocols that underpin website security are HTTP and HTTPS. Both perform the same basic function, but HTTPS is the more secure option. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between HTTP and HTTPS, and why website security has become an increasingly important topic in recent years. We’ll also delve into topics such as SSL certificates, data encryption, and the impact that switching to HTTPS can have on website ranking signals. So, let’s get started!
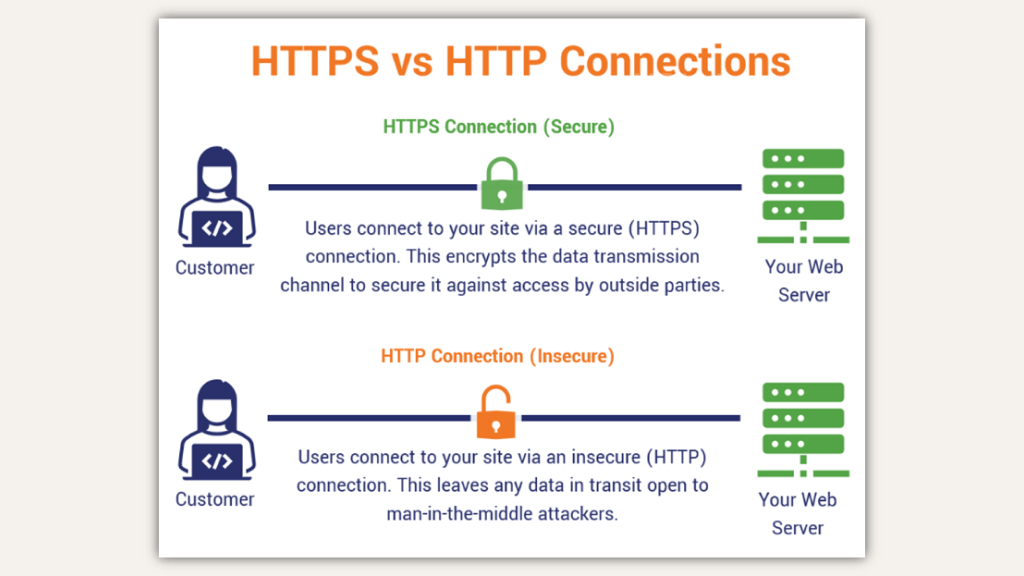
What is HTTPS and Why is it Important?
HTTPS, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, is an internet protocol that ensures secure communication between a user’s browser and the website they are visiting. It is the secure version of HTTP, which allows for the transfer of data between servers and clients on the web.
In order for a website to use HTTPS, it must have an SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificate installed. This certificate is a digital document that verifies the identity of a website and creates a secure connection between the user’s browser and the server hosting the website. This protects users from potential security threats, such as hackers intercepting and accessing sensitive information.
Data encryption is another essential component of HTTPS. This process scrambles any data transmitted between the user’s browser and the website, making it unreadable to anyone who may intercept it. This allows for the safe exchange of sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card details, over the internet.
In today’s digital age, website security is of utmost importance. HTTPS provides an added layer of protection for users, ensuring that their browsing experience is safe and secure. Websites that use HTTPS are seen as more trustworthy and reliable, ultimately leading to a better user experience and increased website traffic.
The Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
HTTP and HTTPS are two protocols that facilitate communication between a user’s browser and a website. However, there are fundamental differences between the two in terms of security and data encryption.
The primary difference between HTTP and HTTPS is that HTTPS incorporates SSL/TLS certificates to encrypt data communications, whereas HTTP does not. This encryption helps protect sensitive information transmitted over the internet, such as passwords, credit card information, and other user data.
| HTTP | HTTPS |
|---|---|
| Unencrypted data transmission | Encrypted data transmission |
| No SSL/TLS certificate required | Requires SSL/TLS certificate |
| Lower website security | Higher website security |
Additionally, using HTTP instead of HTTPS can impact website security, website ranking signals, and the overall user experience. Google has also made it clear that HTTPS is a ranking signal, indicating that websites with HTTPS encryption are favored in search rankings over websites with only HTTP encryption.
Therefore, ensuring a secure website with data encryption through HTTPS is crucial for maintaining website security and user trust in the digital age.
Migrating from HTTP to HTTPS: Why and How?
With the increasing importance of website security, migrating from HTTP to HTTPS is becoming a crucial step for website owners. HTTPS provides enhanced security by encrypting data transmitted between the user’s browser and the website they are visiting, protecting it from potential hackers.
To migrate from HTTP to HTTPS, the first step is to obtain an SSL certificate. This certificate allows the website to establish a secure connection with the users and confirms the authenticity of the website. Once the SSL certificate is obtained, the website’s server settings need to be configured to enable HTTPS. This includes installing the certificate, redirecting HTTP to HTTPS, and configuring SSL protocols and cipher suites.
Updating internal and external links is another significant step in migrating from HTTP to HTTPS. All links within the website should be updated to use HTTPS, and any external backlinks to the website should also be updated if possible. This ensures that all connections to the website are secure and do not result in any security warnings or errors.
It is crucial to implement redirects from HTTP to HTTPS. Failing to do so can lead to negative impacts on the website’s search engine ranking and user experience. Implementing redirects helps to retain the website’s SEO value by ensuring that visitors are automatically directed to the HTTPS version of the website.
In conclusion, migrating from HTTP to HTTPS is an essential step for website owners that care about website security and user privacy. By obtaining an SSL certificate, configuring server settings, updating links, and implementing redirects, website owners can ensure that their website is secure and their users’ information is protected.
Conclusion
In today’s digital landscape, secure browsing and website security have become paramount. With cybercrime on the rise, it is essential for website owners to prioritize data protection and take steps to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. As we have discussed in this article, the key difference between HTTP and HTTPS lies in the level of security they offer. HTTPS, with its SSL certificate and data encryption capabilities, is the preferred choice for modern websites.
By choosing to migrate from HTTP to HTTPS, website owners can help ensure their visitors have a safe browsing experience. It may seem like a daunting task, but with careful planning and implementation, the transition can be seamless. Remember to obtain an SSL certificate, configure server settings, and update internal and external links. It is crucial to implement redirects to avoid any negative impact on SEO during the migration process.
In conclusion, website security and data protection should be a top priority for all website owners. As the internet continues to evolve, the need for secure browsing will only increase. By adopting HTTPS, website owners can provide their visitors with a secure and trusted browsing experience while staying ahead of the competition in terms of SEO ranking signals.
FAQ
What is the difference between HTTP and HTTPS?
HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, while HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. The key difference between the two is that HTTPS uses encryption to secure the data transmitted between a user’s browser and the website they are visiting, while HTTP does not. This encryption is provided by an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate, which establishes a secure connection.
Why is HTTPS important for website security?
HTTPS is crucial for website security because it ensures that data transmitted between a user’s browser and a website is encrypted and cannot be intercepted or tampered with by malicious actors. It protects sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card details, and personal data from being compromised. Additionally, HTTPS helps to establish trust and credibility with users, as they can see the padlock symbol and “https://” in the website URL, indicating a secure connection.
How does data encryption work with HTTPS?
When a user accesses a website that uses HTTPS, their browser and the website’s server establish a secure connection using the SSL certificate. This certificate contains a cryptographic key that is used to encrypt the data transmitted between the two parties. The encrypted data can only be decrypted by the intended recipient, ensuring that any sensitive information remains private and protected.
What are the benefits of HTTPS?
There are several benefits of using HTTPS for a website. Firstly, it provides enhanced security by encrypting data transmitted between users and the website. This helps protect sensitive information from being intercepted by hackers. Secondly, HTTPS is considered a ranking signal by search engines, meaning that websites with HTTPS may have a slight advantage in search engine rankings. Lastly, using HTTPS can help establish trust and credibility with users, as they see the padlock symbol and “https://” in the website URL.
How can I migrate my website from HTTP to HTTPS?
Migrating your website from HTTP to HTTPS involves several steps. Firstly, you will need to obtain an SSL certificate from a trusted certificate authority. Next, you will need to configure your server settings to enable HTTPS. This may involve installing the SSL certificate and redirecting HTTP traffic to HTTPS. Finally, you will need to update any internal and external links to reflect the new HTTPS URLs to avoid any broken links. It is also important to implement redirects from the old HTTP URLs to the new HTTPS URLs to ensure a seamless transition and avoid any negative impact on SEO.
monperatoto
monperatoto
monperatoto
situs togel
situs gacor
situs toto
toto togel
situs slot resmi
slot gacor
slot resmi
togel online
situs toto
togel