What is a VPN? Everything You Need to Know
constantvpn.com – What is a VPN? Discover how Virtual Private Networks protect your online privacy, secure your data, and unlock content. Learn how they work and when to use them.
The internet has made our lives easier, but it comes with a price: privacy risks. From hackers to advertisers, many parties are tracking our online activities.
If you’re wondering how to stay safe, the answer might lie in using a VPN (Virtual Private Network). So, what is a VPN exactly?
In this article, we’ll break down how VPNs work, their benefits, limitations, and why they’re essential for today’s internet users.
What is a VPN?
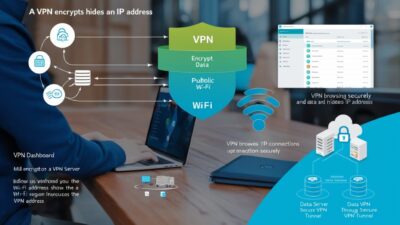
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a service that helps you stay anonymous online by encrypting your internet connection and routing it through a secure server.
This process hides your IP address (the unique identifier of your device) and ensures that your data is encrypted, protecting it from hackers, government surveillance, and nosy advertisers.
Think of a VPN as a private tunnel between your device and the internet. It allows you to browse securely, especially when using public networks, and gives you access to content that may be restricted in your location.
How Does a VPN Work?
VPNs use data encryption to secure the connection between your device and a remote server. Here’s a simplified explanation of how it works:
- Encryption of Data:
- When you connect to a VPN, it encrypts the data traveling between your device and the server. This makes it unreadable to anyone trying to intercept it.
- IP Masking:
- VPNs replace your real IP address with the IP address of the VPN server. This helps you remain anonymous while browsing.
- Secure Tunnel Creation:
- The VPN creates a secure tunnel that shields your data from hackers, especially when using public Wi-Fi at cafes or airports.
- Routing through Remote Server:
- All your internet traffic is routed through the VPN’s server before reaching its final destination. This ensures that your online activity is private and secure.
Benefits of Using a VPN
- Enhanced Online Privacy and Security:
A VPN hides your IP address, making it difficult for websites and hackers to trace your activities. Your data is encrypted, reducing the risk of it being stolen or misused. - Access Geo-Blocked Content:
Many streaming platforms, like Netflix or BBC iPlayer, restrict access based on location. With a VPN, you can change your virtual location and enjoy content from anywhere. - Safe Browsing on Public Wi-Fi:
Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecure and vulnerable to attacks. A VPN secures your connection, protecting your data even when using public networks. - Bypass Censorship and Restrictions:
In some countries, access to certain websites is blocked. A VPN helps users bypass government censorship and access restricted content.
Types of VPNs
- Remote Access VPN:
- This type of VPN is commonly used by individuals to connect to private networks remotely. For example, employees working from home use remote access VPNs to securely access company resources.
- Site-to-Site VPN:
- A site-to-site VPN connects multiple networks, typically used by businesses to link offices in different locations. It ensures seamless communication between different branches while keeping data secure.
When and Why Should You Use a VPN?

- Protecting Personal Information on Public Wi-Fi:
VPNs are essential when using public Wi-Fi, as these networks are vulnerable to cyber-attacks. - Accessing Location-Restricted Content:
Whether you’re traveling or trying to stream shows from another country, a VPN helps you bypass geo-restrictions easily. - Securing Business Communications:
Companies use VPNs to secure remote access to sensitive data and ensure that their employees can work safely from anywhere.
Limitations of a VPN
- Reduced Internet Speeds:
- Since VPNs encrypt your data and route it through remote servers, they can sometimes slow down your connection.
- Limited Anonymity:
- While a VPN improves privacy, it doesn’t make you completely anonymous. Websites can still track you using other methods like cookies.
- VPN Blocking by Websites:
- Some websites and streaming services actively block VPN traffic, which can make it challenging to access certain content.
How to Choose the Right VPN
- Speed:
- Look for VPNs that offer high-speed connections to avoid slow browsing or streaming.
- Security Protocols:
- Ensure the VPN uses reliable protocols like OpenVPN or WireGuard for maximum security.
- Server Locations:
- The more servers a VPN offers, the better your chances of finding a fast and accessible connection.
- No-Log Policy:
- Always choose a VPN with a strict no-log policy to ensure that your browsing data isn’t stored or shared.
- Reviews and Pricing:
- Read user reviews and compare pricing plans to find the best VPN for your needs.
So, what is a VPN? It’s a powerful tool for protecting your online privacy and securing your data from prying eyes.
VPNs encrypt your connection, hide your IP address, and allow you to bypass geo-restrictions, making them essential in today’s digital world.
While VPNs offer many benefits, they also come with limitations, such as reduced speeds and VPN blocks. The key is to choose the right VPN service that fits your needs, ensuring you browse the internet safely and without restrictions.
Whether you’re working remotely, streaming content, or just browsing the web, a VPN is your best friend for secure and private internet access.
FAQs
What is a VPN?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a service that encrypts your internet connection and hides your IP address, providing online privacy and security.
How does a VPN work?
A VPN encrypts data between your device and a remote server, masking your IP address and routing traffic securely to protect your online privacy.
What are the benefits of using a VPN?
Using a VPN enhances online privacy, allows access to geo-blocked content, secures public Wi-Fi browsing, and bypasses censorship.
Does a VPN make you anonymous?
While a VPN improves privacy by hiding your IP address, it doesn’t make you completely anonymous, as websites can track you using other methods.